Scalability and Sustainability of a Surgical Infection Prevention Program in Low-Income Environments
Clean Cut results, published in JAMA Surgery, achieve a 34% relative risk reduction of surgical site infection
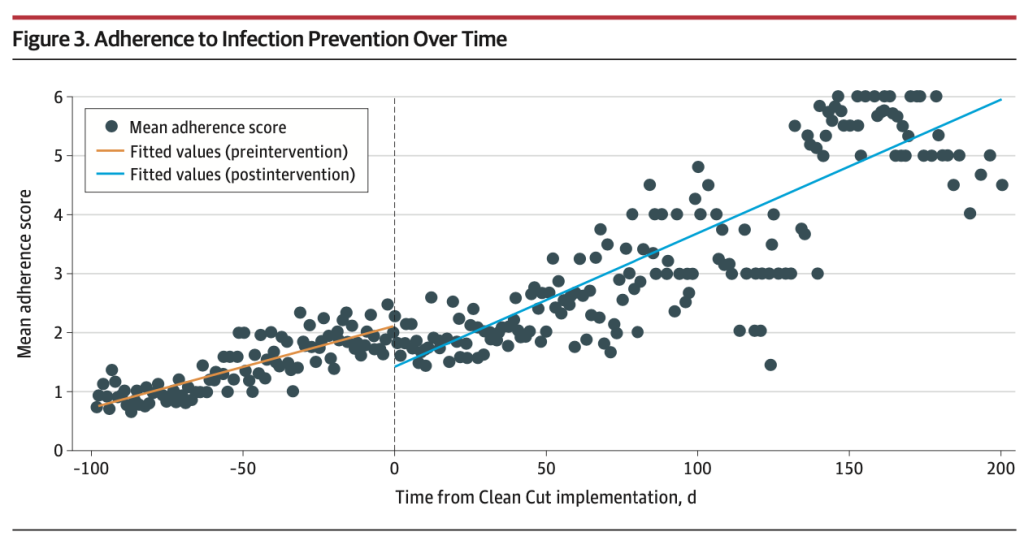
This study found that after the implementation of the Lifebox Clean Cut program, there was a 34% relative risk reduction of surgical site infection.
Published in JAMA Surgery, this study was based on data from 3,364 surgical patients across seven Ethiopian hospitals looking at the results post- implementation of the Lifebox Clean Cut program – strengthening adherence to the six Clean Cut infection prevention standards.
This study used a modified implementation strategy of Clean Cut, reducing external resource and programmatic input from Lifebox, structured education and training materials, and wider hospital engagement. This approach resulted in outcomes that matched our pilot study, with improved adherence to recognized infection prevention standards resulting in a reduction in SSIs but with a model optimized for scalability.
AUTHORS: Nichole Starr, MD, MPH, Natnael Gebeyehu, MD, Maia R. Nofal, MD, MPH, Jared A. Forrester, MD, Assefa Tesfaye, MD, MPH, Tihitena Negussie Mammo, MD, Thomas G. Weiser, MD, MPH, and Lifebox Clean Cut Collaborative.